What Is GST? GST Explained:
What Is GST? All About GST: Full Form | Meaning | Types… Explained
- September 18, 2019
- Posted by: Editorial Team
- Category:

GST Overview
Honestly, keeping up with the new GST data is not a doddle…!!!
Whether or not you focus on GST news, you still may not know all about GST.
But do you know that the layout of LeadingFile can actually help you with all the new GST information as well as new GST registration? Have a graphical vision of the same, here – GST Information Explained.
On & On, the future of GST is clear. Might, this time it is going to subsume the direct taxes too.
All right, but what comes to your mind when you think about GST, Is it a spoiler for you? Too bad.
GST is the only thing which has made the tax filing, so easier. On an approx is it applicable and liked by all the 29 states and 7 union territories.
Reach Out To The Most Common “GST की मूल बातें” At GST Basics…!!!
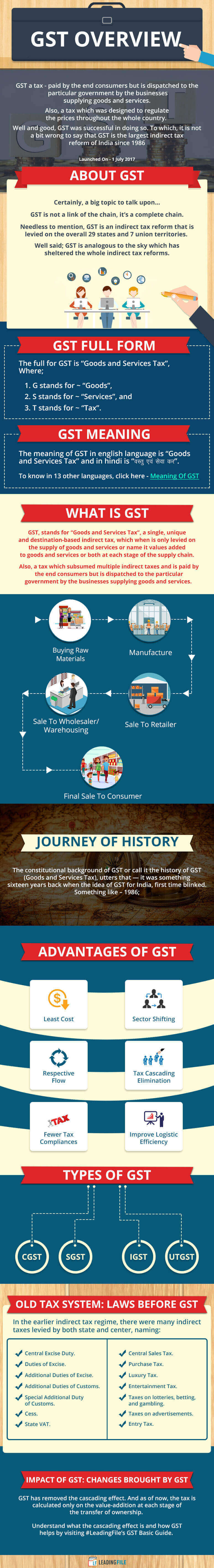
BTW, does anyone from these ‘states and territories’ know ~ for what reason the GST was designed & launched? Well, GST being a “Goods and Services” tax was designed to regulate the prices throughout the whole country.
Well and good, GST was successful in doing so.
Now, it is not a bit wrong to say that GST is the largest indirect tax reform of India since 1986.
These are not our words. The history of GST utters this.
Certainly, it has been something 2 years until the GST launched, and it is still a work in progress. Also, that’s only half the story of GST and the reason behind saying this statement is — GST till has subsumed only the partial tax reform. However, it is done with the complete indirect tax reform but still to be done with direct taxes.
Apart to this, here’s what the GST (Goods & Services Tax) all about that you need to pay attention to, keep going…
About GST: All You Need To Know About GST (Goods & Services Tax)
Certainly, a big topic to talk upon…
GST is not a link of the chain, it’s a complete chain.
Needless to mention, GST is an indirect tax reform that is levied on the overall 29 states and 7 union territories.
Well said; GST is analogous to the sky which has sheltered the whole indirect tax reforms.
So, in order to understand the GST from zero, let’s start from the — Full Form of GST. Here we go:
GST Full Form
The full form of GST is — “Goods and Services Tax”.
Wherein, each and every letter of the word GST has its own word. Have a look…
- G stands for ~ “Goods”,
- S stands for ~ “Services”, and
- T stands for ~ “Tax”.
As a result, these words after encapsulating forms “Goods and Services Tax”.
All right, but what type of tax this is? Ease; It (Goods and Services Tax) is an all in one tax which is imposed in India on the supply of goods and services.
Well, do you know – this imposed tax is not only-but also a major source of revenue for a government.
Consequently, let’s discover how taxes work in India. Have a look…
We all know that the government of any country needs money to survive or for its functioning. But, we aren’t aware of the fact – where this money comes from?
An answer to this is – “TAX”.
Wherein, the tax itself is classified into two types:
- Direct Tax.
- Indirect Tax.
Yes, the major source of surviving and functioning of a government is none other than these taxes. On & On, taxes are a major source of revenue for a government.
On the contrary to this, you must be thinking – what government does with that much tax? Ease; the tax collected by the government is spent on the public for their welfare.
All right!
What next? Nothing big, let’s try and understand the tax classification in detail;
Direct Tax: Definition | Types | Examples | Features
A tax reform which is imposed on the profits or income of a person and is paid directly to the imposing entity. Additionally, the tax should be distinct from that of the tax imposed upon a transaction – which thereby is considered as an indirect tax.
All right! But what those direct taxes are? Have a look at the types of direct tax — income tax, corporate tax, wealth tax, gift tax, expenditure tax etc.
However, the payable tax varies on the income earned by the person from various sources. Sources be like – salary, affiliation, income from house rent, etc, etc.
Therefore, the more you earn — the more tax you need to pay…!!!
Indirect Tax: Definition | Types | Examples | Features
A tax which is imposed on the goods and services instead of income or profits made by a person.
Also, it is a tax which is collected by an intermediary, which further-on himself files the tax return and forward the same to the government along with the returns.
In other words — Indirect tax is a tax which is also known as GST (Goods and Services Tax), now.
Time and again, all right! But, what those indirect taxes are? Don’t panic, have a look at the types of indirect taxes — sales tax, service tax, value added tax, custom duty and octroi tax, excise duty, anti-dumping duty tax, etc.
Well, upon going through the above-mentioned statement, you must be wondering about the meaning of GST.
GST Meaning || Meaning Of GST In Different Languages
The meaning of GST is “Goods and Services Tax”, a value-added tax imposed on the supply of overall goods and services.
Well, this tax (GST) is paid by the end consumers but is dispatched to the particular government by the businesses supplying goods and services or both.
Overall, this is how the government runs its body.
Going forth, if you are a consumer or businessman of India, knowing hardly any language other than your mother tongue, and still trying to figure out the meaning of GST then this heading is only for you, keep going…
The meaning of GST in 13 different languages are mentioned as follows:
- GST Meaning In Hindi: वस्तु एवं सेवा कर
- GST Meaning In English: Goods and Services Tax
- GST Meaning In Bengali: পণ্য ও পরিষেবা কর
- GST Meaning In Marathi: वस्तू आणि सेवा कर
- GST Meaning In Telugu: వస్తువులు మరియు సేవల పన్ను
- GST Meaning In Tamil: பொருட்கள் மற்றும் சேவைகள் வரி
- GST Meaning In Urdu: سامان اور خدمات ٹیکس
- GST Meaning In Gujarati: સામાન અને સેવાઓ કર
- GST Meaning In Kannada: ಸರಕು ಮತ್ತು ಸೇ ವಾ ತೆರಿಗೆ
- GST Meaning In Punjabi: ਗੁਡਸ ਐਂਡ ਸਰਵਿਸਿਜ਼ ਟੈਕਸ
- GST Meaning In Malayalam: വസ്തുക്കളും സേവന നികുതിയും
- GST Meaning In Sindhi: سامان ۽ خدمتتون ٽيڪس
- GST Meaning In Arabic: ضريبة السلع والخدمات
Other than this, let’s discuss what is GST in detail…
What Is GST || GST Working From Manufacturing To Delivery
Literally, modifications are still being uttered about GST and there is no second-guessing that statement.
Time and again, let’s address this with a quick overview…
Something like 2 years back – when the GST was introduced (1 July 2017), it subsumed multiple but bounded indirect taxes into it.
Time changed and as of now, it has replaced almost 17 of the existing state and central indirect taxes.
Also, more to come in the future like — Entertainment Tax, Sale Of Land or Building Tax, Central Excise Duty Tax, Additional Customs Duty Tax, and a lot.
So, it is completely transparent that this is not the end of GST.
Mark: To hear LIVE about the future of GST, visit in the anchor text as: Future Of GST In India: A Report By GST Council/-
Going forth, let’s discuss GST from its root. Commencing it with a question: why it is called GST?
Root consider — as of the indirect tax was applied to the goods and services, so, in order to connect the applicability with naming, it was named GST (Goods and Services Tax).
Well, GST is a single uniform indirect tax which is applied on all small to large-sized businesses.
Mark: Starting things up is a doodle. But, getting things registered is not a bit doodle.
Don’t worry; LeadingFile is only innovated to make things doodle, figure out your business with our MSME Registration; Cheers…!!!
On-going, the quality of being single and unique makes it one of the greatest tax reforms in the country. However, to be a single tax reform, it has replaced numerous indirect tax laws which existed in India before 1st July 2019. And as of now, it is a multi-stage, comprehensive, destination-based tax which is levied on each and every stage of value addition.
Also, now-a-days, it (GST) is one (1) indirect tax for the whole country.
Subsequently, to understand it with an imaginary and orbicular method; join the ongoing article…
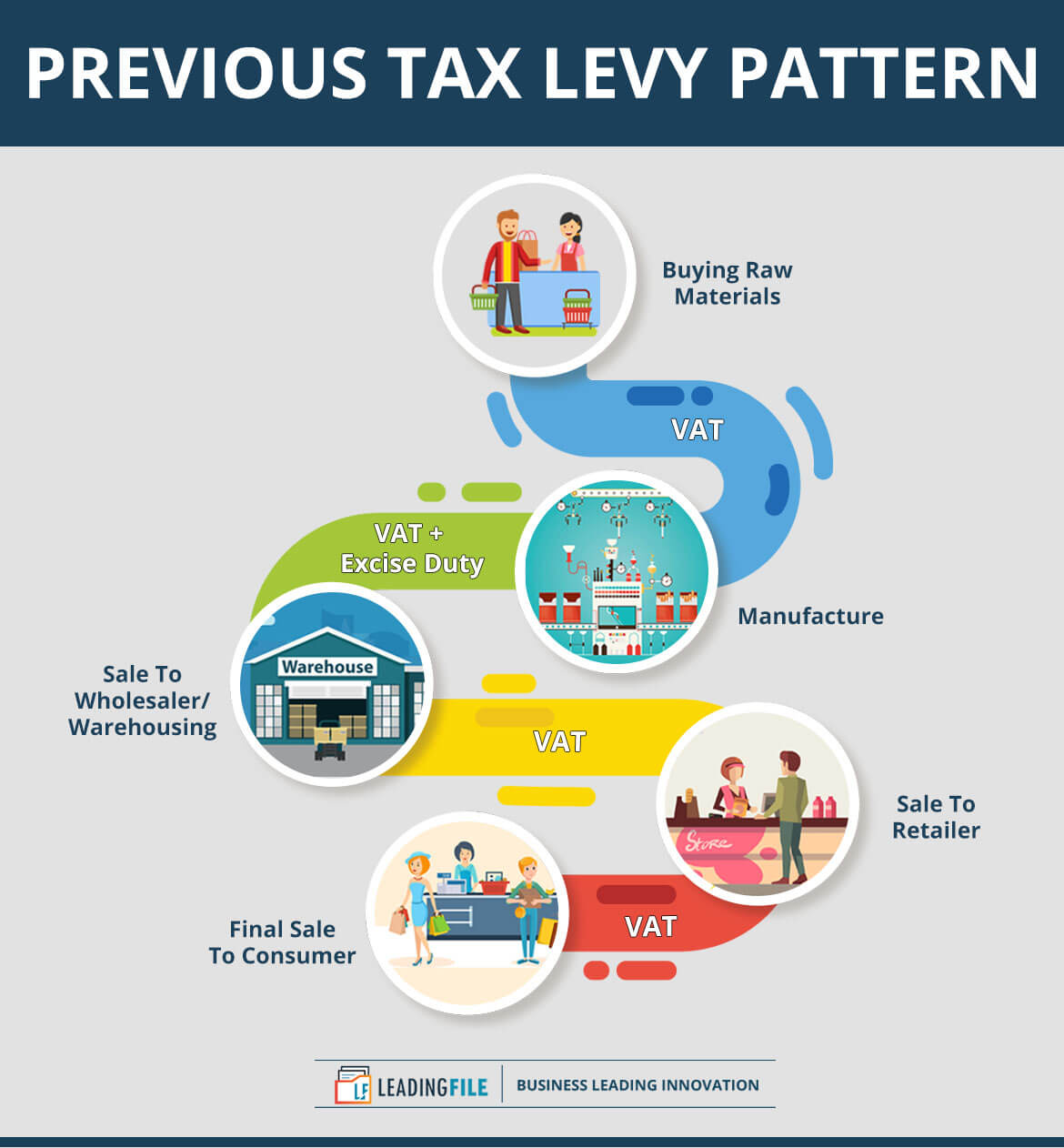
Firstly, let’s figure out the pattern of tax levy which was applied before GST (Goods and Services Tax) era, which we often call – Previous Tax Levy Pattern:
Understood. If not, then try to understand it here.
As appears in the above infographics, from stage first “Buying Raw Materials” to final “Sale To Consumer” — the tax included on each stage is VAT and Excise duty.
In fact, some more of the taxes have to be mentioned as well. But to these stages and to only this infographic, they are sufficient to be mentioned.
After all, this is also not a bit less. Filing this much of taxes may carry off anyone’s mind from the tax filing and finding another theft way to go with.
Mark: Do you understand the importance of tax filing, if yes then you must be e-verifying your returns, regularly. If not, then you aren’t even done with the filing process.
Apart from this, in order to get done with the filing process, e-verify your returns, today @LeadingFile, here: E-Verify ITR: 6 Electronic Methods To Verify Income Tax Return.
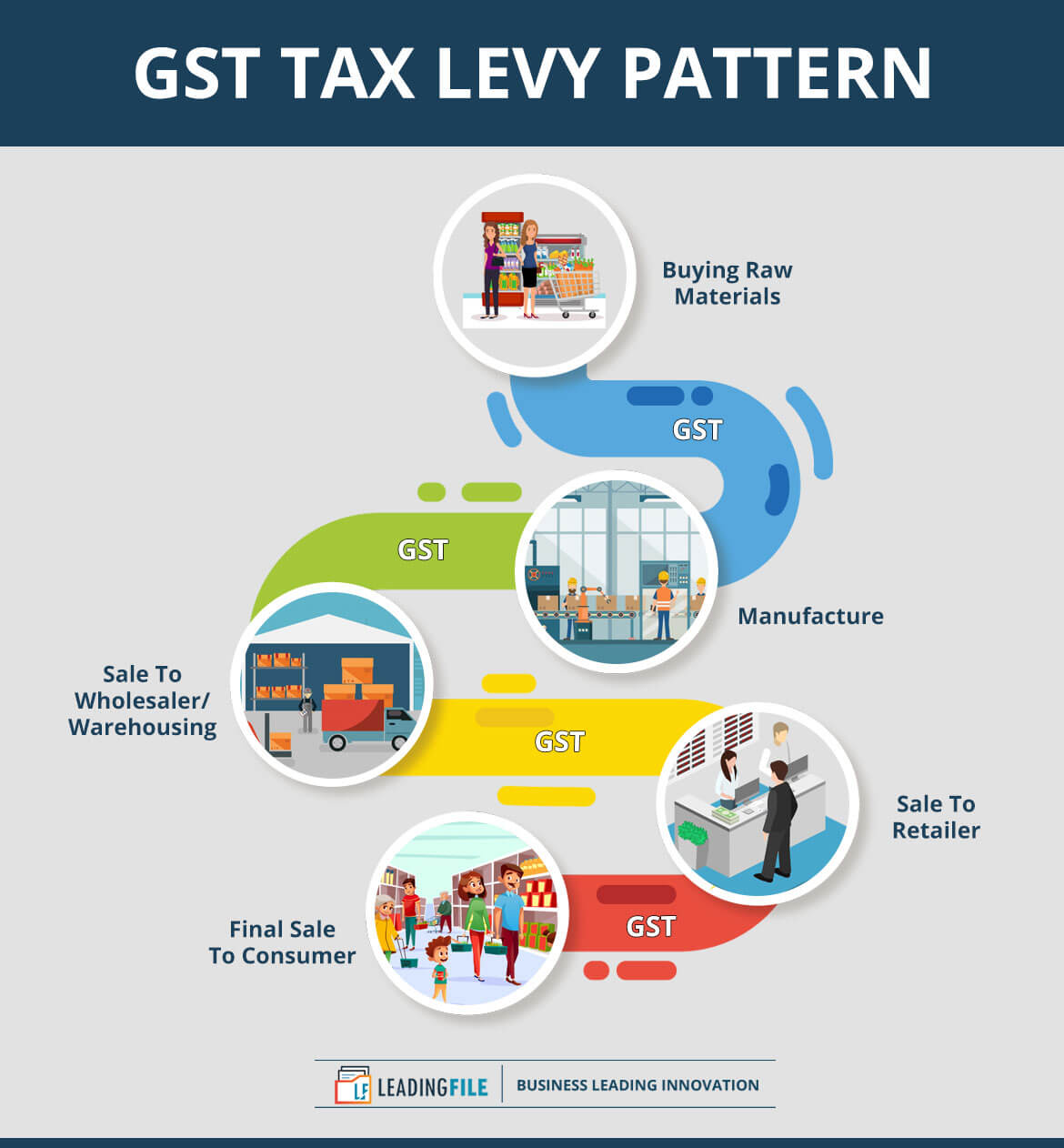
But within time, the government came up with a new tax reform — The GST.
Have a look…
Isn’t it easy and cost-effective? The answer is cut and clear — it is.
An address to this is; taxes levied over the latest pattern (GST) are less and the very phenomenon makes it easy to file and cost-effective too.
Of course, it will be cost-effective (will cost least) if a single tax will be levied on every stage, also with a single and constant percentage.
Now, let’s try to understand the same with its on-going definition statement.
Statement says — GST is a multi-stage, comprehensive, destination-based tax which is levied on each stage of the value addition. and it is so.
Let’s figure out the same statement;
GST: Multi-Stage
All right, we assume Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a multi-stage tax.
But, how it is so-and-so?
Ease; as appears in the above-illustrated infographics — a single product from being manufactured to supply, relocates multiple places with the applicability of GST on each.
Let’s fondle out each place; starting from buying raw material to the end-consumer sale, it relocates five (5) places, as follows:
- To first — the purchase of raw materials (product itself),
- Second — production or manufacture + GST,
- Third — warehousing and sale of finished goods to wholesaler + GST,
- Forth — sale to retailer + GST,
- Fifth — sale to consumer + GST.
So, what do you say now? Isn’t it multistage?
Certainly, Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a multi-stage tax reform, and it seems clearly through-out the above-mentioned theory and infographics.
What next? Next, let’s subsume its second phase of the very definition statement.
GST: Comprehensive
Apart from being multi-stage, it too is comprehensive.
And how it is so and so? Have a look…
Comprehensiveness asks to deal with all the elements of anything and this is only what GST is known for!
Yes, GST is the only tax reform that deals with all the stages of value addition. So, whatever you call GST is “OK” but you just have to call it #comprehensive.
Next, head over to another phase of the same statement i.e — Destination Based Tax!
GST: Destination Based Tax
We agree – it is a multi-stage, comprehensive as well, but how it is destination-based, means how?
Don’t panic, regard an illustration…
Think as — goods (products) manufactured in Mumbai and are sold to the final consumer in Delhi. Going forth, as we all know that GST is levied at each stage of value addition but on the consumption side. So, the tax revenue is supposed to go to Delhi only.
Apparently, the entire tax revenue is going to flow Delhi and not Mumbai. Thus, with this illustration, it is translucent clear that the GST is a destination-based tax.
Now, let’s consider going with the value addition…
Value Addition: GST
This ultimate phase is somewhat the entire stage’s together. Means, somewhat a collaboration of all the stages, together. Hence it involves, the manufacturer, the wholesaler, the retailer and lasts the consumer.
Let’s deal with the working of the same…
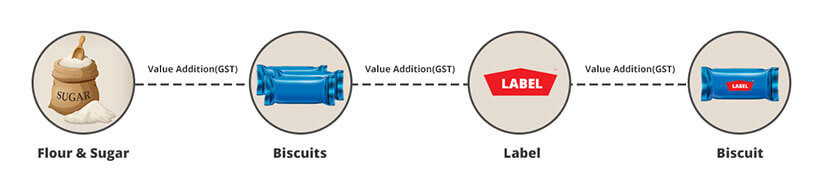
Starting from the end of the manufacturer, who wishes to make a product — biscuit.
So, in order to make biscuits, the manufacturer needs to buy some raw material like – sugar and flour. Upon buying, he will bake sugar and flour to make #biscuits. To which, he will suffer a value addition on the baking of biscuits. And this value addition is going to affect the wholesaler because he is going to buy it from the manufacturer.
Now, the terms are to the wholesaler. Wholesaler upon buying the baked biscuits will pack the biscuits into a fixed quantity and will also label them. More like to the baking process, he (wholesaler) too is going to suffer a value addition on packing and labeling.
And this time, this value addition is going to affect the retailer, because he is going to buy biscuits from the wholesaler.
Subsequently, now the turn is of the retailer, he upon buying the biscuits will pack them in small quantities and even will invest in the marketing of the biscuits. To which, similar to manufacturer and wholesaler, he too is going to suffer a value addition on packing and marketing as well.
But this time, this value addition is going to affect the end consumer.
Now, you might be wondering about the GST, don’t you? Have patience; GST is here only…
Actually, GST is levied on the value addition of each biscuit production stage or you may name it — the monetary value added at each production stage to gain the final sale to the end consumer.
So, the statement that “GST is a tax reform which is paid by the end consumers but is dispatched to the particular government by the businesses supplying goods and services” has been proven true.
All right! What now? Nothing big, let’s discuss out the journey of GST in India, so-long…
Journey Of GST In India: Path Mapped By GST
Let’s call it — GST history so far.
Also, it might not be a bit off-ward to say the journey, a history so far.
Well, the constitutional background of GST or call it the history of GST (Goods and Services Tax), utters that — it was something sixteen years back when the idea of GST for India, first time blinked. Something like – 1986.
Quite older the GST is, Don’t you think so? If not then traverse the path so-long mapped by GST via a infographics:
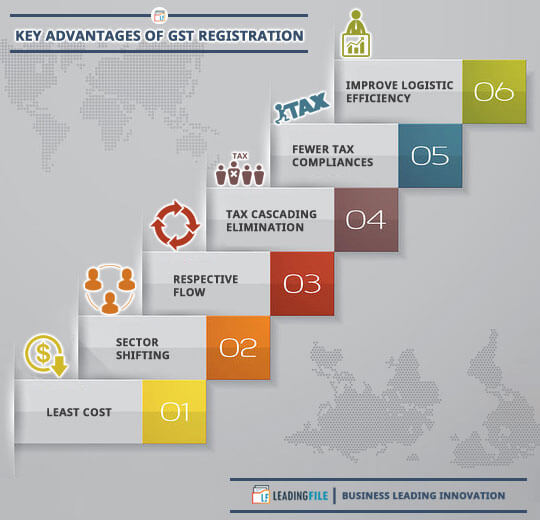
GST Benefits In India: Know – What Are The Advantages Of GST?
Just think of it this way: If GST would not have removed all indirect taxes and you were asked to file all indirect taxes respectively, what do you think was going to happen to your savings?
They would have ended by now.
With this, it is translucent clear that GST has a ton of benefits.
But, all of them cannot be mentioned here. To name a single: Cascading effect.
The blunder benefit of GST arrival is cascading effect removal. Yes, GST has removed the cascading effect on the supply of overall goods and services.
An address to this is – GST regime has eliminated the tax on tax system and now the entire country is enjoying the GST taxation system.
Note: In order to know more about the taxation system, visit the URL here – Tax Structure In India: An Overview Of Taxation In India.
Also, the thing is GST is complete a paperless and technological driven system. This all stuff makes it, money like beneficial.
Some other benefits are here…
Upon retrieving the advantages, now, let’s walk towards the components of GST (Goods and Services Tax), as…
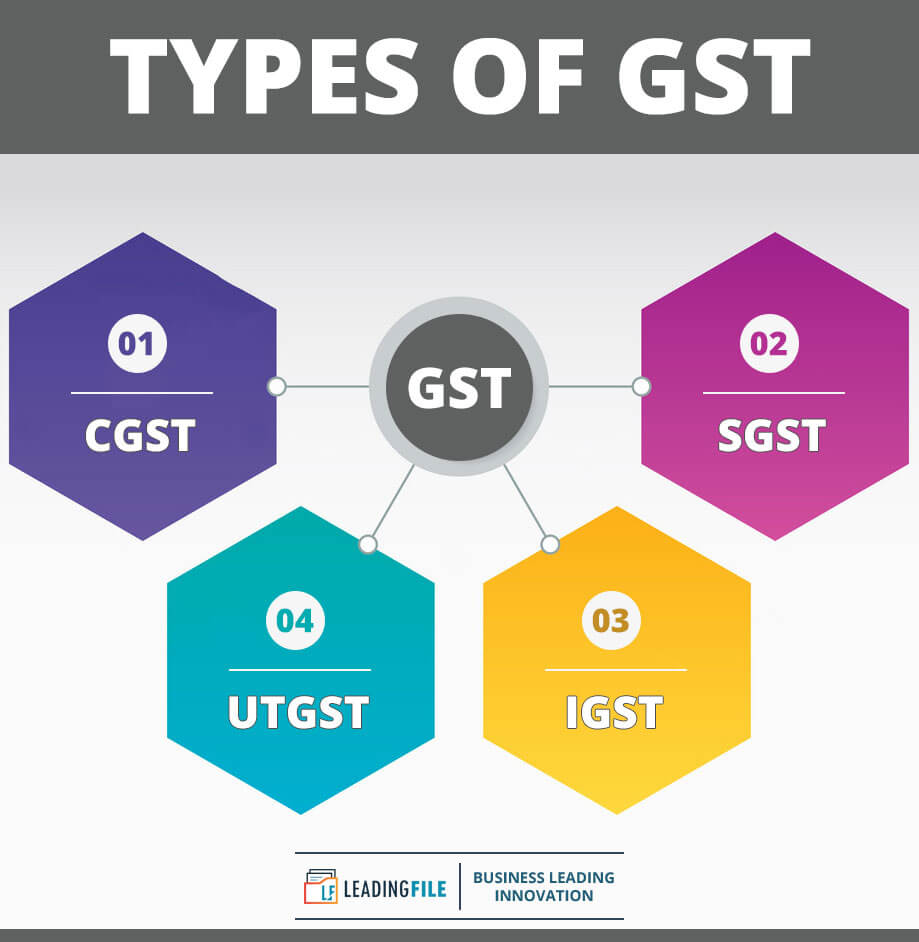
Types Of GST: Replicate GST Types Via Day-To-Day Life Example
A coin has two sides, similarly, GST is also a coin that holds two sides. On which, 3 taxes components are described on one side and 4 on the other side.
However, applicable are only 3, but the way the coin is sold with both sides, similarly GST is also known for the 4 taxes components.
Here they are: CGST || SGST || IGST || UTGST. Have a graphical vision…
Now, let’s formulate them:
- CGST: It stands for “Central Goods and Services Tax”, a tax which is collected by the central government on the intra-state sale.
Illustration; Transaction happening within Mumbai.
- SGST: It stands for “State Goods and Services Tax”, a tax which is collected by the state government on the intra-state sale.
Illustration: Transaction happening within Mumbai only.
- IGST: It stands for “Integrated Goods and Service Tax”, a tax which is collected by the central government but for the inter-state sale.
Illustration: Transaction happening between Mumbai and Delhi.
Understood this? If not, let’s try to understand it with an image…
Not understand yet? Don’t panic, let’s try to understand this with a day-to-day life example…
Day-To-Day Life Example
Scenario: 01 –
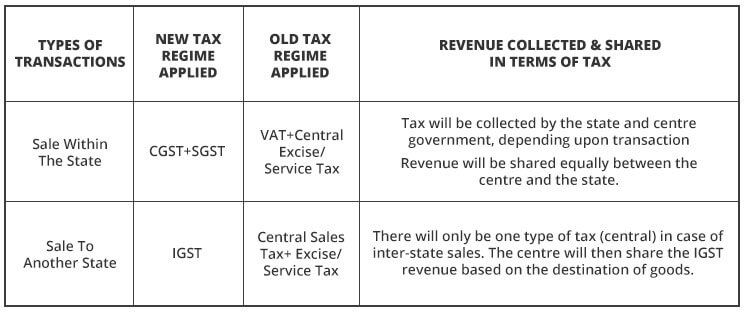
Suppose; Ankush is a dealer in Mumbai, he sold the goods (baked biscuits) to Shadab (dealer) in Delhi worth Rs. 50,000.
To this supposition, the tax regime applied is only IGST and the tax rate to IGST is 18%.
Thus, with the applicability of IGST, the revenue that will go to the central government will be Rs. 9,000.
Scenario: 02 –
Suppose; Ankush the same dealer from Mumbai sells goods (baked biscuits) to Ankit (consumer) in Mumbai only worth Rs. 50,000.
To this supposition, the tax regime applied is CGST + SGST and the GST tax rate to both CGST + SGST is 6% + 6%, each, which comprises a total of 12%.
Thus, with the applicability of CGST + SGST, the revenue that will go to the central and state government will be a total of Rs. 6,000. Out of which, Rs. 3,000 will be given to the central government and Rs. 3000 will be given to the Mumbai government as the sale is done within the state only.
Perhaps, this time you must have understood everything. Long story short, this is all about the new taxation system in India.
Reading this, one might be wondering about the tax laws which were levied before the GST applicability. Here they are, keep going…
Old Tax System: Laws Before GST
Actually, old is gold. But in this situation, it isn’t so.
BTW, you know what – people are dancing to the same song, they used to cry to.
Admirably, it is true!
Alas, they might have known that they are still going with the same old tax system.
Don’t you think so? Oh, so poor of you.
All right! Let me explain everything…
What is comprised of GST, all indirect taxes and what you were filing within the old tax system, all indirect taxes?
Wait, what I just read. Is the old tax system, #GST.
Ya, you read it right.
GST is a new form made from the old tax system which subsumed all the indirect taxes into it.
The only difference is — with GST you file them all at a time and with the old tax system you filed them one by one.
So, the thing is, you are going with the same tax system, only the manner is different. LOL…
Well, let’s give that a depth overview;
Under the old tax system, there were many indirect taxes levied by both state and central government.
Wherein, what the state government collected is — taxes in the form of VAT, which commonly stands for “Value Added Tax”. Also, the problem was, each and every state had a different set of rules and regulations towards the tax collecting laws.
Jumping over the next government i.e central government, what they collected is — taxes on interstate sales of goods. Not to say, they were involved in each case of interstate sales.
But, this is not the end of the indirect taxes list, there were more to come.
Let’s have a view of the same list which will make you aware of the all pre-GST regime indirect taxes…
- Cess
- Entry Tax
- State VAT
- Luxury Tax
- Purchase Tax
- Duties of Excise
- Taxes On betting
- Central Sales Tax
- Taxes On Lotteries
- Entertainment Tax
- Central Excise Duty
- Taxes On Gambling
- Taxes On Advertisements
- Additional Duties Of Excise
- Additional Duties Of Customs
- Special Additional Duty of Customs
Alike a mountain! Similar was the replacement of taxes and the upcoming GST. But, anyhow — CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST managed to replace all these mentioned taxes and GST got placed on 1 July 2017/-
All right! But, did it impact anything? A big – YES, keep going to hear the same…
Impact Of GST: Changes Brought By GST
If you are really curious to know what changes have come from the GST regime, then rub your eyes, open them widely and keep them here…
GST is the only tax regime that has successfully removed the cascading effect.
By reading this statement, you might be wondering what is a cascading effect? In short, it’s a tax on tax.
Haven’t you heard this? Oh come-on, you yourself had still been filing that – tax on tax.
Didn’t remembered yet.
Ok! Let me try to remind…
Within the old tax system, if you were a purchaser or end-consumer then you must have paid the tax. That tax was none other, the tax on tax or name it the cascading effect.
Needless to say, every buyer including the final consumer paid tax on tax within the old taxation system.
But, now it is not so and the effect has been removed by the GST (Goods and Services Tax).
Going forth, as of now, the tax is calculated only on the value-addition at each stage of the transfer of ownership.
Long story short, GST is the finest tax reform!
GST Information Explained: Graphical Vision
In order to go with academic discipline, visit — Theoretical GST Overview Guide…!!!

![Why GST: The Need Of GST [By - GST Council]](https://www.leadingfile.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Why-GST.jpg)